What is concrete admixture?
Concrete admixture is a substance that is added to improve the performance of concrete before or during the mixing of concrete. The amount of concrete admixture is generally not more than 5% of the amount of cement.
Because it can effectively improve the performance of concrete and has good economic benefits, concrete admixtures have been paid more and more attention in engineering. The selection, addition method and adaptability of concrete admixtures will seriously affect the performance of concrete.

The use premise of the concrete admixture
The proportion of concrete admixtures should be determined according to the changes of the pouring environment, climatic conditions and external conditions. Therefore, the selection of admixtures should be in line with the requirements of on-site use, to ensure the quality of concrete and to reasonably control the project cost.
Mixing design
Generally, the strength of concrete needs to be set according to the part used in the project. Concrete engineering strength grade requirements, the physical and chemical properties of admixtures, and the types of admixtures should be considered to meet the design requirements of various indicators.
On-site testing
After the concrete ratio is tested in the laboratory, since the actual situation on site is inconsistent with the parameter values set by the laboratory, the admixture ratio should be adjusted appropriately to meet the needs of actual on-site use.
The amount of admixtures used
The amount of admixtures used has an important influence on the performance of concrete. The usage amount should go through the process of precise calculation, scientific ratio in the laboratory, and on-site adjustment, and finally get a reasonable usage amount.

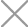
Concrete admixtures types and their functions
Because admixtures can effectively improve the performance of concrete and have good economic benefits, they are widely used in many countries and become an indispensable material in concrete.
There are 16 kinds of common concrete admixtures, which are roughly divided into 5 categories according to their functions.
Water-reducing admixture: Under the condition that the slump of concrete is basically the same, it can reduce the water consumption in the mixing process.
Early strength agent: Accelerates early strength development of concrete and has no significant effect on later strength.
Retarder: Extend concrete setting time.
Air entraining admixture: A large number of tiny air bubbles are generated during the mixing of concrete.
High-efficiency water reducing admixture: Under the condition that the slump of concrete is basically the same, it can reduce the water consumption in the mixing process.
Early strength water reducing admixture: It has the functions of early strength agent and water reducing admixture.
Retarding and water reducing agent: It has the functions of both retarder and water reducing admixture.
Air entraining and water reducing agent: It has the functions of both air entraining admixture and water reducing admixture.
Anti-reducing agent: Reduce the water permeability of concrete under hydrostatic pressure.
Anti-corrosion admixture: Inhibit or mitigate corrosion of steel bars or other embedded metals in concrete.
Air-entraining agent: During the production of concrete, a large number of pores are formed in the concrete due to the chemical reaction and the release of gas.
Expanding agent: Cause the concrete to expand a certain volume.
Anti-freezing agent: Make concrete harden at negative temperature and achieve sufficient frost-resistant strength within a specified time.
Colorant: Production of concrete with stable color.
Accelerating Admixture: Make concrete harden quickly.
Pumping agent: Improve the pumpability of concrete mixes.
The role of admixtures in improving the performance of concrete

- It is possible to reduce the amount of water used in the concrete, or to increase the flow of the concrete without adding water.
- Adjust the setting time of concrete.
- Reduce bleeding and segregation, and improve workability and water elutriation resistance.
- Reduce slump loss and increase concrete pumpability.
- Reduce shrinkage, and adding expansion agent can also compensate for shrinkage.
- Delay the initial hydration heat of concrete, reduce the heating rate of mass concrete, and reduce the occurrence of cracks.
- Improve the early strength of concrete and prevent freezing under negative temperature.

- Improve strength, and increase frost resistance, abrasion resistance and corrosion resistance.
- Control the reaction between alkali and aggregate to prevent steel corrosion and reduce chloride diffusion.
- Concrete with other special properties can be made.
- Reduce concrete viscosity.
Precautions when using concrete admixtures
The amount and usage of admixtures have strict application environment and restrictions. Its usage should be taken into consideration from the actual conditions of the construction site, concrete construction technology, and climatic and environmental factors, and it cannot be used arbitrarily.
It is an important premise to choose the appropriate type of formal admixture, and avoiding the purchase of counterfeit and shoddy products will affect the progress of the project. For the admixtures used, it is necessary to strictly check whether the quality meets the actual requirements of the construction site, carefully read the product instructions, and conduct multiple proportioning tests in the laboratory, and also meet the requirements of material quality inspection specifications.
Different parts of the concrete project on the construction site have different requirements for the strength of the concrete. Moreover, the chemical reaction effect of the same admixture in cement applications with different properties is also different.
Therefore, the selection of cement varieties has become an important quality control link. The laboratory should also carry out comparative tests on the chemical reaction effects of different types of cement in the same admixture. The amount and scope of use of admixtures should not only be based on previous construction experience, but should be based on test results to ensure that the use meets quality requirements.
Before using concrete admixtures, it is necessary to control the quality of the engineering structure. Moreover, the chemical characteristics of the admixture should be tested by a professional testing laboratory, such as the physical and chemical properties of the expansion agent, the magnesium oxide content, the total alkali content, the ammonia content in the chemical properties, and the fineness in the physical properties, etc. If it meets the quality requirements, then proceed to the next trial matching test.

Influence of concrete admixtures on slump
Under normal circumstances, the operator will add a certain amount of water reducing agent to the concrete to achieve the purpose of increasing the slump of the concrete, which can effectively improve the workability of the concrete.
Experiments show that concrete without water reducing admixture loses less slump in 1 hour than concrete with water reducing admixture. The main reason for this phenomenon is that the concrete needs to go through the processes of mixing, transportation and pouring after adding the water reducing admixture.
Therefore, it is necessary to use the method of adding water at the construction site to restore the slump of concrete that has been added with water reducing admixture. However, this method will significantly reduce the strength and other properties of concrete, which may lead to concrete cracking, abnormal hardening and other phenomena.
In order to effectively solve the problem of slump loss of concrete mixed with water reducing agent, it is recommended to use methods such as adding water reducing agent in batches.
Among the above-mentioned methods, the batch mixing method can not only effectively avoid the problem of concrete slump loss, but also control the production cost to a certain extent and maximize the benefits of concrete construction.

The current application problems of concrete admixtures
Compatibility of concrete admixtures with concrete
The choice of concrete admixtures greatly affects the performance of concrete, so the choice of concrete admixtures determines whether the admixtures are compatible with concrete, and then determines whether the project can be carried out with high quality.
Therefore, the choice of concrete is particularly critical. First determine the concrete properties required for the construction conditions, then select the type of admixture required and conduct compatibility experiments.
Different admixtures have functional specificity and cannot be used in place of each other, otherwise it may lead to negative effects. At the same time, the materials used in concrete, such as cement, sand and gravel, admixtures, etc., must meet relevant industry standards.

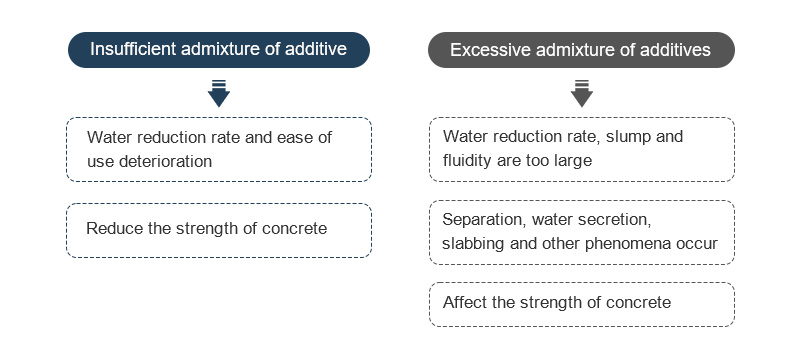
The relationship between the amount of concrete admixture and concrete strength
The strength of concrete is closely related to the amount of concrete admixtures. Insufficient admixtures will lead to poor water reduction and workability of concrete. It will also cause the initial slump and expansion of the concrete to become smaller, reduce the strength of the concrete, and cause construction difficulties.
However, if the amount of admixture is excessive, the water reduction rate, slump and fluidity of the concrete may be too large, and segregation, bleeding, and hardening may occur when the concrete is left standing, which will affect the strength of the concrete.
At the same time, the addition of excessive admixtures may also affect the hydration process of concrete. If too much retarder is added, the setting time of concrete will increase and the progress of the project will be affected.
Repulsion between concrete admixtures
During concrete production, various concrete admixtures can be added to improve the performance of concrete. Usually, admixtures have functional specificity, but when using two or more admixtures, attention should be paid to the mutual adaptability of their functions. If the functions of the two admixtures are not compatible, they may have opposite effects.